Hacked Webpage Finder
Drop In Traffic? Seeing Strange Things On Google?
We Will Scan All Your Pages For Hacks
Ensure the integrity of your website with Hacked Page Finder, the ultimate web-based tool designed to detect signs of hacking and malicious activity on your site. By performing a thorough scan of your web pages, Hacked Page Finder identifies suspicious elements, helping you safeguard your digital presence.
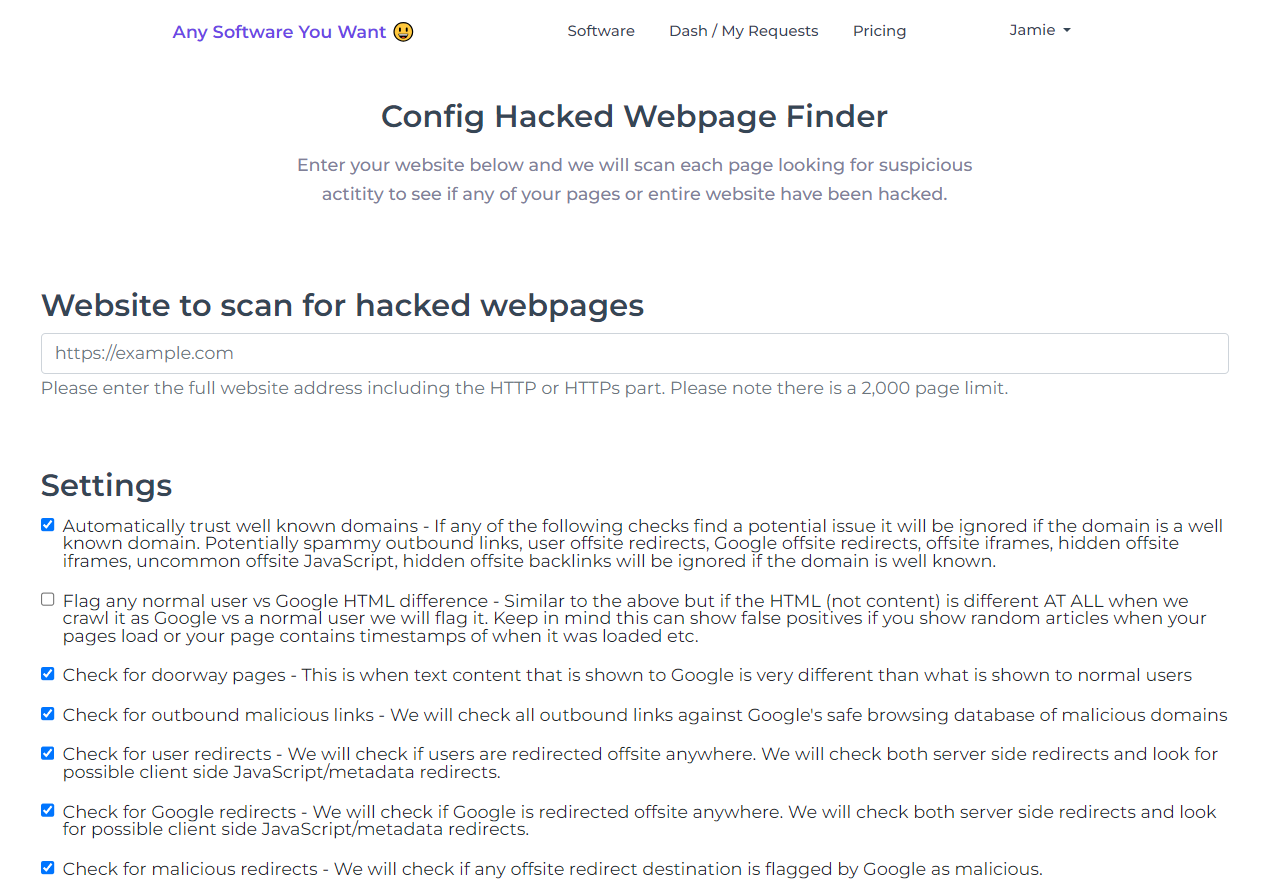
Simply enter your website and configure a small amount of settings then click start. Here are just some of the checks it performs:
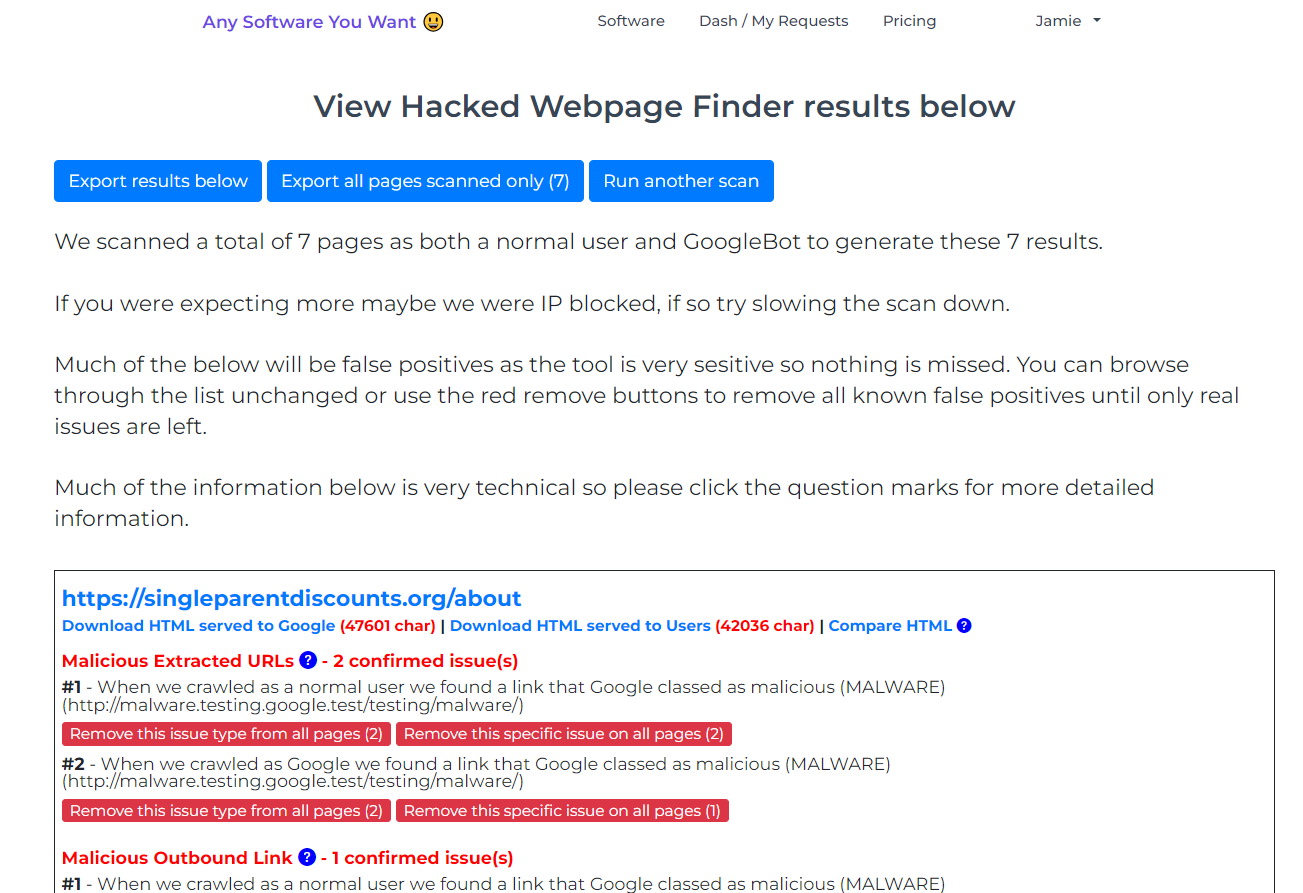
1. Malicious Extracted URLs
Our tool scans the HTML of each page, identifying and extracting all external URLs, including those embedded in JavaScript, JSON, and schema markup. These URLs are then checked against the Google Safe Browsing project for any signs of malicious activity, including phishing, unwanted software, malware, and viruses.
2. Hidden Blocks
We compare how each page appears to both a normal user and GoogleBot. Hackers often manipulate content visibility differently for users and search engines to conceal their activities. This check highlights any discrepancies, allowing you to investigate further.
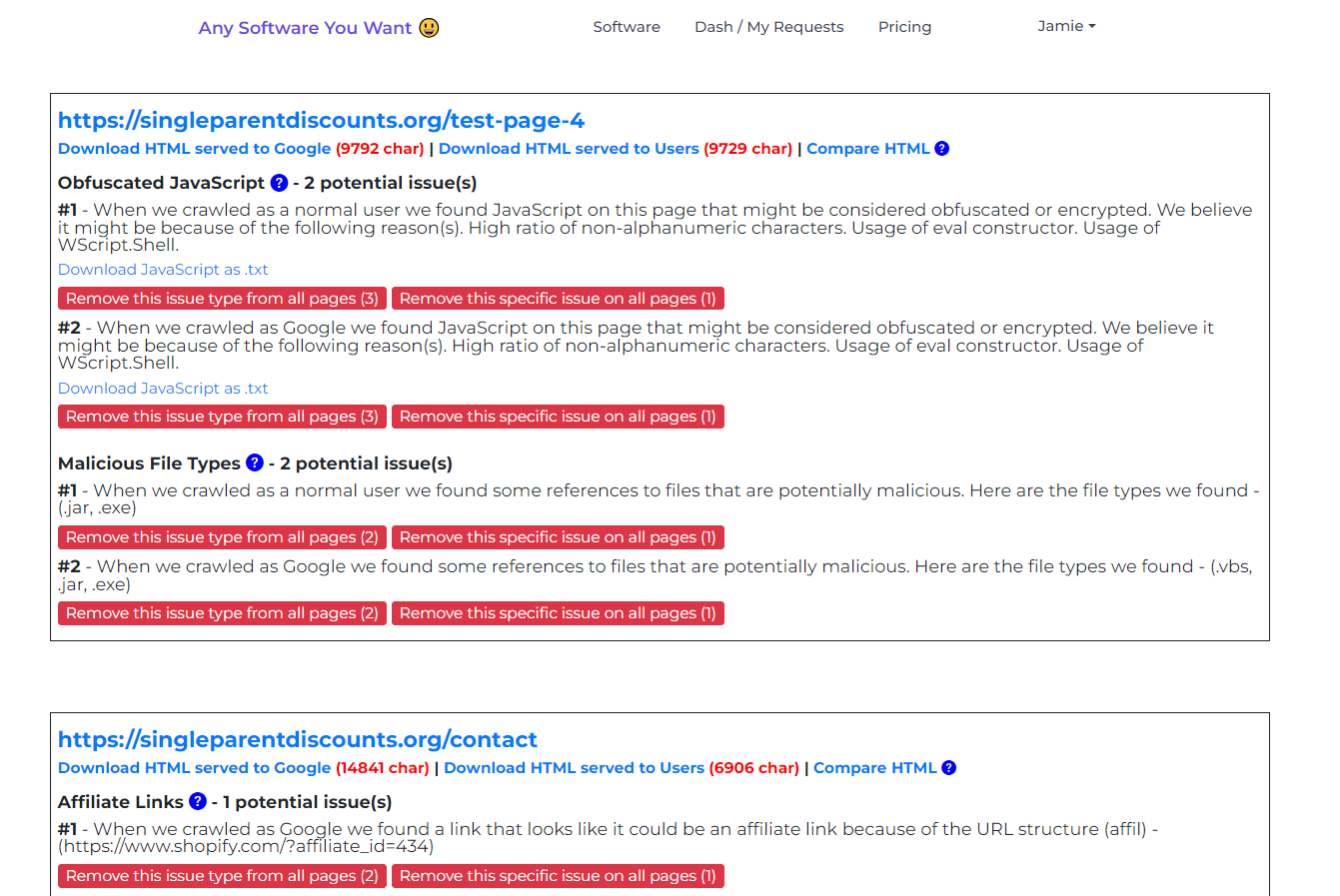
3. Malicious File Types
This scan identifies references to potentially dangerous files, such as .exe files, within your web pages. If your website doesn't typically reference these types of files, it's a red flag worth investigating.
4. Compare and Download HTML
Use our tools to compare and download the HTML content served to both GoogleBot and normal users. Differences may indicate hidden content or other anomalies, providing deeper insights into potential security issues.
5. Offsite JavaScript File
We detect any offsite JavaScript files included in your pages, which could be indicators of Cross Site Scripting (XSS) attacks. Investigate any unfamiliar scripts to ensure they are not malicious.
6. Offsite Redirect
We track if internal URLs on your website redirect to external domains. While often legitimate, unexpected redirects to unknown domains should be examined closely.
7. Push Notification API Usage
Our scan checks for the use of the Push/Notification API in your web pages. If your site doesn’t use this feature but it’s detected, further investigation is warranted.
8. Offsite iframe
We identify any external iframes within your pages. Unrecognized iframes might be used for malicious purposes, such as initiating automatic downloads.
9. Obfuscated JavaScript
This check detects JavaScript that appears obfuscated or encrypted, a common technique used by hackers to conceal malicious code. Download the flagged scripts for a closer look.
10. Hidden Link
We examine external links presented to GoogleBot and normal users, as well as those hidden using CSS tricks. Hidden backlinks are a common tactic used by hackers to boost their own sites’ SEO.
11. Hidden iframe
Similar to hidden links, we check for discrepancies in iframes visible to GoogleBot versus normal users. Hidden iframes can conceal malicious content while still driving traffic.
12. Hacking Signature
Our tool scans for typical hacker signatures, such as “hacked by” messages. While some keywords might result in false positives, this check is vital for identifying explicit signs of a breach.
13. Foreign Content
We detect significant amounts of non-English content on your pages, which can indicate automatically generated pages left by hackers.
14. Doorway Page
We compare the content shown to normal users and GoogleBot, identifying any different content, a tactic used by hackers to avoid detection while manipulating search results.
15. Affiliate Links
This scan identifies external links that appear to be affiliate links. If you don’t participate in affiliate programs, these links might have been placed maliciously.
16. Spammy Outbound Link
We check for outbound links pointing to potentially spammy websites. While there can be false positives, this check helps identify and mitigate spammy or harmful links.
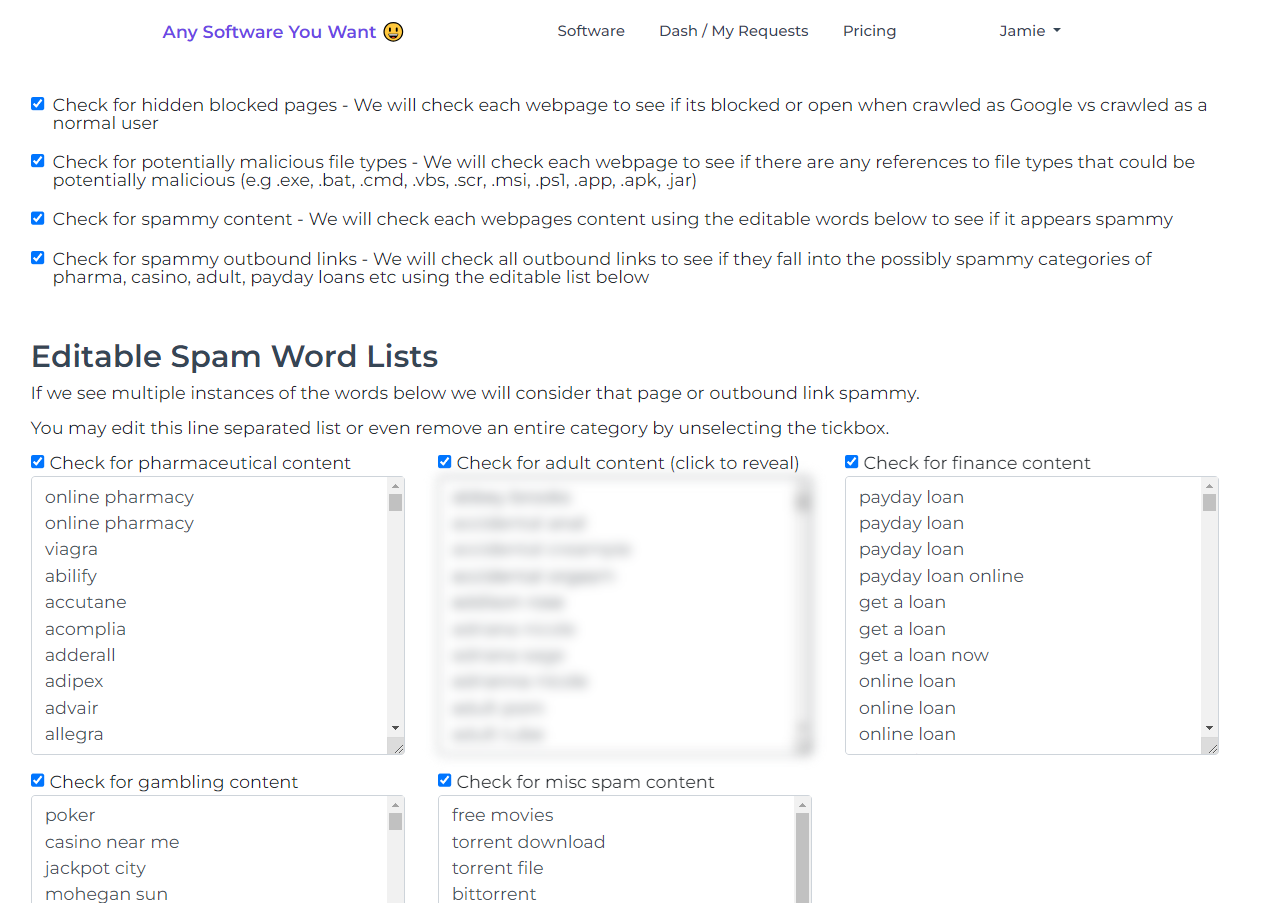
17. Spammy Onsite Content
We scan for words commonly associated with spammy niches, such as gambling or adult content. Though often false positives, this check remains sensitive to avoid missing any injected spam.
18. Malicious Offsite Redirect
This check tracks internal URLs redirecting to external domains, verifying if the destination is flagged by Google Safe Browsing as malicious.
19. Malicious Outbound Link
We scrutinize all outbound links to ensure they aren’t flagged as malicious by Google Safe Browsing, signaling a potential hack.
20. Malicious Internal URL
Every page on your website is checked against the Google Safe Browsing project for signs of being flagged as hacked or malicious.
21. Malicious iframe
All iframes on your pages are checked against Google Safe Browsing, ensuring they aren’t flagged as malicious.
With Hacked Page Finder, you gain peace of mind knowing your website is thoroughly scanned and protected from potential threats. Regular scans and detailed reports help you maintain a secure and trustworthy online presence. Stay one step ahead of hackers with Hacked Page Finder.
Hacked Webpage Finder Demo Video
What does Hacked Webpage Finder look like?